Eat the Colors of the Rainbow
Alcohol & Weight Loss
Alcohol & Weight Loss | After Your First Two Drinks
After your first drink, your body starts to get rid of the alcohol quickly using the alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) pathway.1 In this pathway, ADH converts the alcohol into acetaldehyde, which gets further broken down to acetate. These by-products (acetaldehyde and acetate) are considered to be highly reactive and can increase oxidation throughout the body, but especially in the liver.
Because your body sees these by-products as dangerous, it wants to use them as fuel.This means your body will significantly blunt fat-burning close to 75% after just one and a half drinks.2 And it will stop using carbs for energy. Therefore, although very little alcohol will be stored as fat (less than 5%), the fat and carbs you are eating have an increased risk of being stored as fat.
Your liver can process these toxins through the increased use of certain vitamins, such as the water soluble vitamins B1, B3, B6, folate and C, while also possibly depleting some of the fat-soluble vitamins, A, E and K1. Over-time these decreases in vitamins can play a secondary role in loss of motivation, energy, and well-being.
After your first couple of drinks, your brain also starts to increase its usage of GABA. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain and is a large reason why alcohol is known as a “depressant.” Over time, the GABA receptors get used to the effects of alcohol, which is a reason why people may need more and more alcohol to feel the effects from alcohol consumption.3 GABA is also the neurotransmitter, principally responsible for allowing you to stay asleep. Therefore when your brain uses more of it before you go to sleep, you have less while you’re actually sleeping, causing a disruption in restful sleep.
Alcohol also affects the higher processing areas of the brain, the cerebral cortex, while leaving the lower areas of the brain somewhat unaffected. This leaves you more emotional than you would normally be. If you’ve ever experienced “drunk logic” while doing or saying things you would never think to do sober, then you’ve experienced the inhibitory effects of having your cerebral cortex taken out of the equation.
While your body has started to use the alcohol as energy, your body releases anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) to help your body rid itself of the alcohol. This basically means that your urine volume increases significantly (about 100 ml per 10 grams of alcohol).4 If you’ve ever “broken the seal,” you know that the more you continue to drink, the more frequently you use the restroom.
Since your kidneys are working over-time, your body releases an increase in certain minerals and electrolytes especially calcium, magnesium, copper, selenium and manganese. All of these play important roles not only in blood volume, but in bone health, blood pressure and the anti-oxidant pathways.
In addition to everything above, a small increase in cortisol typically occurs with moderate drinking while testosterone levels will drop about 6.8% in men (not so much in women).5 Aromatase will also increase. Aromatase is an enzyme that helps to convert testosterone to estrogen and is obviously not something that is welcomed by many guys.
Alcohol & Weight Loss | After Six to Eight Plus Drinks
If you’re drinking a moderate amount of alcohol, those things listed above are the main effects, at least short-term. If you drink heavily and drink often, another system called the Microsomal Ethanol-Oxidizing System (MEOS) system kicks in at the point when the ADH pathway becomes overwhelmed.
This system is interesting because it causes your body to generally burn off more energy as useless heat and probably saves your life from too high of a blood alcohol level. It is primarily controlled by a special enzyme that plays an important role in utilizing certain medications and the metabolism of fatty acids. This increased rate of medication breakdown can decrease their effectiveness, while the incomplete breakdown of fatty acids can cause an increase in oxidation. This increase in oxidation becomes exacerbated as the body’s main anti-oxidant (glutathione) is also impaired, decreasing your ability to fight the oxidation.
As your drinking levels continue to increase, testosterone levels drop from 6.8% with 4 drinks to 23% with 8 drinks.6 This drop, combined with a slowdown in protein synthesis, can cause havoc when trying to recover from a workout.
In addition to that, fluid loss will generally become more significant, causing dehydration that might affect you for days afterwards. Finally, with heavy drinking, the breakdown of alcohol can occur for up to 48 hours after your last drink. This means less glucose is reaching your brain and working muscles, making you both more tired and quicker to fatigue if you do exercise.
If You’re Going to Drink Alcohol, Drink in Moderation and Not Too Often
You would think after listing all that happens in your body after consuming alcohol, the no-brainer suggestion would be to not drink. What is missing though are some of the benefits from consuming moderate amounts of alcohol.
Alcohol is shown to increase insulin sensitivity, which basically means that your body needs less insulin to do its job. In addition to that, research has shown that women who drink a moderate amount will have the same or slightly lower BMI, as those who don’t drink.7 The same effect is not seen in men. Those who moderately drink are also at less risk of dying from heart disease and cancer while decreasing one’s risk of Alzheimer’s8and even slightly improving your immune system.9
In other words, complete abstinence may not be needed while trying to lose fat as long as it’s done in moderation and not very often (think one time per week). If you don’t drink, obviously don’t start, but if you want to have a couple of drinks on the weekend, there is nothing necessarily wrong with having one or two. In future articles, I will list some of the best and worst drinks to have when going out and 5 strategies you can implement to decrease the deleterious effects of having a night of heavy drinking.
Alcohol & Weight Loss | Wrapping It Up
In any fat loss plan, there are three main components that should be priority: Diet, Exercise, and Sleep.
As stated throughout the article, a moderate amount of alcohol can increase total calories, decrease your motivation for exercise, and negatively affect your sleep. Despite this, many people can enjoy a drink or two, without throwing those three components completely out of whack.
On the other hand, drinking heavily can significantly derail energy levels, has a larger influence on dehydration, negatively impacts hormonal levels, and can significantly disrupt your sleep. Therefore, limit your overall levels of alcohol and put yourself in the best position to reap some of the benefits of alcohol consumption, while not derailing your overall progress.
Eat the Whole Egg
An egg is superior to the same quantity of any other kind of food. People who order egg-white-only omelets are missing out on the most nutritious part of the egg: the yolk. Dr. Chris Masterjohn points out that of all the nutrients in an egg, the yolk contains 100% of the fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, D, and K) essential fatty acids DHA and AA, and carotenoids. The yolk contains over 80% of the nine nutrients (calcium, iron, phosphorus, zinc, thiamine, folate, B6, B12 and pantothenic acid), whereas the white contains over 80% of just three nutrients (magnesium, sodium and niacin). Six other nutrients are split more evenly between the two. Of course, the yolk also contains 99% of the fat, which is why people avoid it. Despite the widespread fear of cholesterol, eating eggs has not been shown to cause cardiovascular disease. Egg yolks from pastured hens are a deep orange, unlike the pale yellow of conventional yolks, and are richer in nutrients. as well as tasting better.
L-Glutamine vs. Glutamine
Q. What is the difference between L-glutamine and glutamine, and the same for the other amino acids? Is one more effective as a supplement than the other?
A. Unfortunately the answer to this question will involve some chemistry, though it may not be necessary to completely understand all the chemistry to understand the gist of the answer.
All the amino acids in our bodies have a common structure that enables them to link up to one another by what is known as a peptide bond, producing the long strands of amino acids that we define as proteins. Without these long protein chains we could not survive. Amino acids are constructed so that two mirror images can exist, like your right and left hands. If you have ever tried to put a left-handed glove on your right hand you can see how difficult it would be for a "right-handed" amino acid to connect to a "left-handed" amino acid.
Louis Pasteur observed the "handedness" of amino acids and many other molecules in our bodies. He found that when you shine a beam of polarized light through a solution of amino acids, the light beam would be rotated counterclockwise. The amino acids are thus designated "levo" (left) or " " amino acids. A minor problem was that not every amino acid rotates light counterclockwise even though they all had the common chemical structure that allows them to link up. Pasteur solved the problem by calling all amino acids "L" amino acids (the capital letter is important) whether they actually rotated light clockwise or counterclockwise.
Whether the "L" prefix is present or not, all the glutamine that is found in our food or food supplements is L-glutamine because the mirror image of L-glutamine (called D-glutamine for "dextro" or right) has no nutritional value and is useful only for chemical lab research.
D-Amino acids occur in nature in small amounts. All the amino acids that are made into proteins are L-amino acids, but some bacteria use D-amino acids in their cell walls to help them resist the natural antibiotics that are produced by other bacteria. Mostly D-amino acids in foods are the product of bacterial fermentation and so are found in products such as yogurt and cheese. D-Amino acids in the amounts found in food are generally thought to be harmless to humans.
One D-amino acid has been proposed to have benefits in the human body, not for protein synthesis but as a pain reliever. D-Phenylalanine, the mirror image of L-phenylalanine, is not normally found in the body but may have a pharmacological effect on the production of enkephalins, the natural pain relievers our bodies produce in high-stress situations. The third World Congress on Pain recommended trials of D-Phenylalanine for pain relief, but unfortunately there have as yet been no "double-blind-placebo-controlled" studies, which are necessary to establish the credibility of a treatment for most clinicians. A mixture, DL-phenylalanine, is much more readily available than D-phenylalanine because it is cheaper and easier to make. DL-phenylalanine may also be an effective antidepressant drug on a par with imipramine, one of the first and, for a long time, the standard antidepressant in psychiatry. In clinical studies, DL-Phenylphenyl worked faster and with fewer side effects and was about as effective as imipramine. You should always check with your health care provider before trying DL-phenylalanine.
Calcium
The recommendation of calcium for the prevention of osteoporosis is one of a multitude of examples of how often the current practice of mainstream medicine is missing the mark. Many people are deficient in calcium because the standard acidic processed diet is high in hidden phosphates from processed foods which inhibit the absorption of calcium. In addition, by eating large quantities of meats and sweets, this makes the body acidic. This acid requires a huge amount of buffering. When the plasma buffer reserves are exhausted, the body calls upon calcium from the bone to buffer. Hence, eating phosphate laden processed foods causes calcium loss from bones.
To build bone, calcium is laid down in bone only when enough of the complementary minerals are present, such as zinc, copper, boron, and magnesium. When these are not present in optimal amounts, taking extra calcium merely deposits the calcium in the toxic waste heap of the body, the blood vessel wall. So instead of building bone, the calcium is used to accelerate arteriosclerosis, aging and disease.
In other words, by haphazardly recommending calcium to a nation of people who are already consuming vast quantities of cheese, milk, ice cream and meats, and without measuring the blood levels of zinc, copper, magnesium, we are potentiating the development of vascular calcifications instead of bone calcification. We are enhancing the deposition of extra calcium in the vessels of the heart and brain that hastens coronary artery disease, arteriosclerotic and nutrient-deficient depression, and senile brain disease.
Beware if you are supplementing with Calcium as it cannot get into the bone unless you have enough of the other minerals needed to incorporate it and hold it in the bone. These include magnesium, manganese, selenium, molybdenum, zinc, copper, etc. Taking calcium without assessing and correcting for deficiencies of these minerals, forces the calcium into the arteries of the body in the brain and in the heart. When you are deficient in the minerals that hold calcium in the bone, calcium cannot be taken up into the bone. SO instead it gets taken up by the toxic waste site; the cholesterol patches of damaged arteries. Hence the term hardening (calcification) of the arteries.
Problems from Omega-3 Fatty Acid Deficiency
According to a recent study at Harvard University - omega-3 fatty acid deficiency is officially one of the top 10 causes of death in America. Many deliberating health conditions such as cancer, osteoarthritis, metabolic and cardiovascular diseases can be traced from the imbalance of omega-3 and omega-6 consumption in our diets. Unhealthy or inadequate diet is often blamed and assumed to be the cause of omega-3 deficiency. Unfortunately, it's a much more complex problem than you might think.
1) Consuming adequate amounts of omega-3 through diet is difficult. Omega-3 fatty acids are primarily found in fish and shellfish. Studies have shown that if you take less than 2-3 portions of oily fish (cold-water fish) per week, having omega-3 deficiency is very likely.
2) Lifestyle and dietary factors influence the body's natural ability to produce omega-3 fatty acids. This includes drinking alcohol/coffee, smoking, stress, high saturated fat intake and diabetes.
Eating at least 2 portions of fish every week is not an easy task, let alone staying away from coffee and alcohol. To make things worse, not all fish are equally beneficial when it comes to omega-3 intake. Cold-water fish, such as mackerel, herring, salmon and tuna has the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids. It's safe to bet that most of us are omega-3 deficient. No wonder omega-3 deficiency is the sixth biggest killer of Americans and more deadly than excess trans fat intake. Below are some of the signs and symptoms which may indicate that you are suffering from fatty acid deficiency:
*Sleep problems (difficulty in falling asleep and/or waking up in the morning) *Excessive thirst and/or frequent urination *Attention disorders (poor concentration levels, ADHD) *Emotional sensitivity (depression, mood swings, unexplained anxiety) *Rough or bumpy skin *Dry, dull or brittle hair and dandruff *Soft, peeling or brittle nails
Top 6 Health Benefits Of Fish Oil
Health benefits of fish oils come from the presence of omega-3 fatty acids like Docosahexaenoic (DHA) and Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). There has been a lot of hype about fish oil. One, because it's a powerful dietary supplement but two, fish oil manufacturers have marketed fish oil as a remedy for virtually everything. In fact, fish oil serves a huge market and there are countless brands and manufacturers that try to outsell one another. I will talk more on this subject later but first, let's have a look at the scientifically proven benefits of fish oil.
Anti-inflammation
Everyday foods like bacon, eggs, coffee and dairy products all cause inflammation in our bodies. Inflammation is present and occurs in us all the time. If we don't have this under control, things can get out of hand fast and result in serious health conditions.
Fish oil is effective in reducing inflammation in the bloodstream and tissues. According to the Cardiovascular Research Institute in Maastricht in Netherlands, "fish-oil fatty acids with anti-inflammatory properties can help prevent and reverse a plethora of cardiovascular diseases." Furthermore, fish oil is found to be effective in treating gastrointestinal disorders, celiac disease and irritable bowel disease (IBD). This comes without surprise as inflammation is known to cause all of these problems (and so much more). Unlike most other supplements, even the FDA recommends and allows claims for omega-3 for heart diseases!
Osteoarthritis
A study from the University of Bristol suggests that omega-3 fish oil significantly reduces the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis. It was found that omega-3-rich diets fed to guinea pigs, which naturally develop osteoarthritis, reduced the disease by 50% compared to those who ate standard diets.
Cancer
Yes, there are actual scientific studies that suggest fish oil is great for cancer prevention and cancer treatment! This alone immediately qualifies fish oil as an essential part of our diet as approximately 39.6% of men and women will be diagnosed with cancer at some point during their lifetime. Studies have proven that fish oil helps to kill various cancers including colon, prostate and breast. What's more interesting is that DHA (omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil) not only kills cancer cells as a standalone treatment, but can also enhance the effects of anti-cancer drug therapies.
Depression
Fish oil is known to relieve depression disorder symptoms, anxiety, restlessness and stress. In the journal of Nutritional Neuroscience, a paper was published testing the effects of fish oil on adolescents with major depressive disorders. It was found that fish oil intake resulted in 40% decrease in major depression symptoms along with marked improvements in the nutrition content in the brain. You would be interested to know that countries where fish is frequently consumed have the lowest incidences of depression!
Eye Disorders
Fish oil is also known to improve vision and help to avoid age-related eye disorders such as cataracts and age-related macular degeneration. Researchers from France evaluated 290 patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and discovered that their dietary fish oil and seafood consumption were significantly lower in AMD patients. Today, the National Eye Institute at the National Institute of Health in the United States is planning a nationwide study to confirm the findings above. This study will provide even stronger evidence and allow government agencies and physicians to recommend fish oil for macular degeneration.
Brain Function
Researchers have found strong correlations between fish oil supplements and cognitive functioning. One study performed in Holland followed the dietary habits of 342 men from 1990 to 1993 and assessed their rate of cognitive decline during that period. Many different dietary factors were assessed and results clearly showed that only high fish consumption seemed to prevent a decrease in cognitive function. Another study performed on rats showed that there was a clear association between fish oil and brain volume in two important areas - the cerebral cortex and hippocampus - used for memory and thinking.
What To Look For When Shopping For Fish Oil Supplements
Not all health products are made equal and this is absolutely the case for fish oil supplements too. At Transforming Adjustments, one of our mission is to hand-curate a line of high-quality health products that simply works. Today's market for health products are seriously over-saturated and many consumers make the mistake of buying products that have no real value. So what's important to look for when shopping for fish oil supplements?
Fish oil is obtained from almost all fish. They can be from freshwater, farms, ocean, deep sea and shallow sea fish. What's important is that all of these can be heavily contaminated with traces of heavy metal wastes and other toxic compounds. Fish oil must be in their purest forms. Many companies now provide ultra refined or distilled fish oil, but you still need to check if their production standards have been followed. To save your time, we've done the homework for you. Check out OmegAvail Ultra below:
The Core. What is it? And why should you care?
Core exercises are an important part of any strength training program, especially for those just starting out. Many people think that the occasional crunch will be enough to solve any issues they have when it comes to a lack of core strength, however this approached leaves many muscles of the core neglected. Let’s find out why…
What is the Core?
The core is often thought of as just the abs, which makes it understandable as to why sit-ups are seen as the go-to exercise. Unfortunately, it is not that simply. Think about the core as a muscular box where the abdominals make up the front, the paraspinals and gluteals sure up the back, the diaphragm as the roof, and the pelvic floor and hip girdle musculature as the floor.
This intricate construction can be understood simply as the body’s foundation for movement. It is the central region providing a girdle of strength and connecting the abdomen with the lower back and hips. These muscles, together with the spinal muscles, create a stable base for generating strength and providing support for all movement.
Core Anatomy:
- Abdominals – the abdomen is a group consisting of four muscles: The rectus abdominis, also known as the “six-pack” is a superficial muscle sitting on the outermost layer of the core and is mainly involved in flexion. The transversus abdominis, which rests under the rectus abdominis, wraps around the core holding it together like a girdle and works to maintain good posture. Often times the in people with lower back pain the transversus abdominis is very weak. The internal obliques are deep muscles that help the body to rotate and flex to the side. The external obliques are another superficial musculature of the core just above the internal obliques which are important for rotational movements and side flexion.
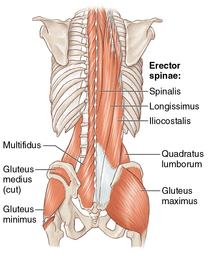
- Paraspinals – made up of two major groups of lumbar extensors: the erector spinae and the “local” muscles (multifidus, rotatores, and intertransveri). The erector spinae is a group of three long tendinous muscles that run the entire length of the spine which provide support for spinal flexion (bending forward), extension (bending backwards) and aid in stabilizing the spine against lateral movement. The “local” muscles, mainly the multifidus is set deep and attached to the spine so that they may work to keep the spine straight and help stabilize through maintaining good posture.
- Hip Girdle & Gluteal Musculature – playing an important role within ambulatory activities such as stabilization of the trunk and pelvis and by transferring force from the legs to the pelvis and spine. The hip musculature consists of the psoas muscle group and the gluteus muscle group. The psoas, also referred to as the hip flexors, control flexion movements at the hip such as walking, running and climbing stairs. And for the gluteal musculature is made up of three muscles: the smallest being gluteus minimus, which lies beneath the gluteus medius, and works to lift the leg outward (abduction) as well as to internally rotate the hip. The gluteus medius sits just above the minimus, it assists with abduction, rotation (both internal and external) and provides stability to the pelvic region. The gluteus maximus is the largest of the three, it works to abduct and extend the hips in addition to stabilizing the pelvic region.
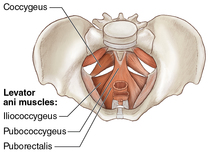
- Diaphragm & Pelvic Floor – The diaphragm serves as the roof of the core by providing stability to the lumbar spine via contraction during breathing. The pelvic floor musculature is coactivated with any transversus abdominis contraction and assists in stabilizing during movement.
- Quadratus Lumborum – A large, thin, quadrangular-shaped muscles that directly inserts into the lumbar spine. The quadratus lumborum works to stabilize the spine against lateral movement, lifting heavy objects and carrying items in one hand.
Why should we care about strengthening the core?
Strengthening the core musculature fights structural imbalances leading to such discomforts as low back pain which is one of the major forms of musculoskeletal degeneration in the adult population, affecting upwards of 80% of all adults. Research has shown that lower back pain is predominant among those who work at a desk, as sitting for long of time in a chair can cause the important muscles of the core to atrophy. Therefore, developing strength within this musculature is essential for maintaining a healthy posture, and leading a pain-free life.
What is an example of a core strengthening exercise?
Sliding Rollout from Knees
- Assume a kneeling position. Place both hands out in front of you on something that can move freely. An ab wheel, a Swiss ball, floor sliding discs or small hand towels will work. Think about squeezing all those muscles we just learned about and keep the head and neck in a neutral position.
- Lower your body under control by extending the hips and flexing the arms until your body approaches the floor. Keep the core and especially the gluteals contracted forcefully.
- Rise back to the starting position.
*The rollout is one of the best core strengthening exercises for beginners. If you use proper form and keep the core contracted, preventing the pelvis from rotating forward, your lower abdominals will receive even more of a workout. Break into this exercise gradually and make sure you keep the body in a straight line at the bottom of the movement. Many people sag at the hips or allow too much anterior pelvic tilt during the rollout exercise.
Just remember, core exercises should be seen as ones that not only help your “six-pack” but strengthen your lower back and pelvis. Having all these work together in harmony leads to better balance and stability, whether you’re on the field playing or completing daily activities.